Yuda Saydun
Recent Posts

Just when I thought it might be time to relax and coast a little as I moved to California, I chose to dive deeper into AI, enrolling in some Stanford classes that promise to stretch my understanding beyond its limits. This is despite the fact that I've been speaking about the subject and preaching about “AI vs AI” for almost a decade. What would prompt me to, once again, grab a backpack, sack lunch, and hit the classrooms?
The decision wasn't just about adding another credential; it was about embracing the future and ensuring my skills remain sharp and relevant. As one of my most respected mentors taught me a few moons ago, "If you keep up, you'll be fine. If you pause for even three months, you'll be obsolete."
The State of AI in Education

Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the education sector, bringing a wave of innovation that enhances student engagement and improves educational outcomes. The integration of AI tools in educational contexts is becoming more widespread, with schools and institutions adopting AI-powered solutions to support both teaching and learning. Generative AI, in particular, has garnered significant attention for its ability to create customized learning materials and personalized learning experiences. This technology is not just a futuristic concept; it’s actively shaping the way educators approach their craft, making learning more interactive and tailored to individual student needs.
Current Challenges
Despite the promising potential of AI in education, several challenges need to be addressed to fully harness its benefits. One of the primary concerns is the lack of professional learning opportunities for educators. Many teachers need the necessary skills to effectively integrate AI tools into their teaching practices, which can hinder the adoption of these technologies. Additionally, there are significant concerns about student data privacy. The use of AI systems in education raises questions about how student data is collected, stored, and used, with the potential for these systems to exacerbate existing biases and inequalities. Furthermore, the high cost of developing and implementing AI-powered solutions can be a barrier for many schools and institutions, making it difficult to access these advanced tools.
Obsolescence Avoidance through Generative AI Education

While technology-focused education has always been a passion, I feel it has never been more important than this particular moment in time, as we are witnessing the advent of mass use of AI and its exciting, ever-evolving spheres of associated knowledge. It’s not enough to simply be aware of AI when its associated vectors, like Machine Learning, large language models, and even neural networks, blossom into new discoveries at a never-before-seen pace.
As founders, board members, and CEOs, we set the tone for our entire organization. Our approach to learning and adapting to AI cascades throughout the company, influencing how our teams perceive and embrace change. It’s crucial that we demonstrate a commitment to continuous learning, not just in words but in actions, which includes prioritizing AI training to ensure our teams are well-prepared to navigate its challenges and opportunities.
I know that in order to continue creating a safer online environment for people and businesses, we must have current, practical knowledge to bolster what decades of experience have already taught us.
Of course, we have all witnessed other technological breakthroughs during our lifetimes… the personal computer, mobile phones, internet connectivity, the cloud, advances in healthcare, and surgical methods.
➡️ The best technologists and innovators in any sector are those who never stop learning. They know technology doesn’t wait for them to have time to “catch up.” Instead, the most impactful and successful technologists have perpetually run alongside the ever-ticking secondhand of advancement and innovation.
Learning is a dynamic and fluid process in which sometimes, yes, an academic whitepaper is read, but other times, this may look like simply taking the time to learn from a colleague in conversation. Many wouldn’t necessarily think of themselves as lifelong learners but simply people who follow a natural curiosity that is often focused on their passions and interests.
Many Paths to Learn More About AI

One of the best things about our connected age is that it has made knowledge in many formats generally accessible, including insights into the latest AI technologies.
Though I am currently enrolled in college courses (some online and others in-person), there are many ways to stay abreast of the latest uses, innovations, and discoveries of AI and its various applications. Educational technology plays a transformative role in enhancing learning outcomes through adaptive programs and data analysis. Whether an employee upskilling to leverage new AI-based tools in the workplace or a C-suite level innovator, this vastly expanding knowledge base is now accessible to all.
In addition to formal Stanford courses, I’ve found the following educational resources to be helpful in my quest to further my AI knowledge.
AI Education via Formal Workforce Training and Professional Learning

Formal training is making up a large part of AI education at the moment, as we are witnessing the rapid evolution of entire swaths of the workforce. Collaboration with school leaders is essential to ensure safe AI practices and enhance the learning environment for teachers and students. From customer service representatives to entire accounting, sales, and marketing floors of multinational corporations, organizations and individuals are realizing the necessity of continuing education AI.
If you’re interested in formal education in AI for your teams, I suggest you look into Correlation One‘s training programs. Their platforms are easy to navigate, and they have programs for workforce development, enterprise upskilling, or individual learners. Training is approached from a foundational level that gives context to the information provided. Their Generative AI readiness toolkit is a prime example of this.
Self-Guided or Independent Learning for AI Knowledge and Student Progress

Opportunities to learn about the AI ecosystem and its less-technical aspects—such as its potential societal impact or possible future applications—abound in the thousands of AI books that were released seemingly overnight.
Finding an engaging read (or listen, if you prefer audiobooks) by a credible source can be a daunting prospect. This curated list is a good place to start. Some books explore the technical and scientific aspects of AI, like Why Machines Learn: The Elegant Math Behind Modern AI by Anil Ananthaswamy. Others offer guidance to business leaders, like The AI-Savvy Leader: Nine Ways to Take Back Control and Make AI Work by David De Cremer. Still, other recent books examine and question the potential socioeconomic impact of this transformative technology as Parmy Olsen does in Supremacy: AI, ChatGPT, and the Race that Will Change the World
Finally, professional and social networks can be an invaluable guide to finding useful information about whatever specific facet of AI education you're looking to pursue. In addition to knowledgeable recommendations, sometimes social media posts from respected industry leaders can be tremendously helpful. An excellent example of this includes this LinkedIn post and a helpful infographic from Denis Panjuta.
Transforming the Learning Experience

AI has the potential to transform the learning experience in profound ways. By creating customized learning materials and providing personalized feedback, AI-powered tools can help teachers identify areas where students need additional support. This enables educators to provide targeted interventions, significantly improving student progress. Moreover, AI can increase student engagement by offering interactive and immersive learning experiences that cater to different learning styles and abilities. Imagine a classroom where each student receives a tailored educational experience, keeping them motivated and engaged. This is the future that AI technology promises.
Generative AI in Education
Generative AI stands at the forefront of educational innovation, offering the potential to revolutionize how we create and deliver learning materials. This technology can help teachers develop tailored lesson plans and educational resources that meet the specific needs of their students. By automating tasks such as grading and feedback, generative AI can also reduce the workload of teachers, allowing them to focus more on direct student interaction and support. The ability to generate customized content on demand means that educational resources can be more dynamic and responsive to the needs of the classroom.
Creating Customized Learning Materials

Generative AI can be a game-changer in creating customized learning materials, such as textbooks, worksheets, and educational games. This technology allows for the development of personalized learning experiences that cater to the individual needs and abilities of each student. By reducing the cost of developing and implementing educational resources, generative AI makes high-quality education more accessible to students from diverse backgrounds. Imagine a world where every student has access to materials that are perfectly suited to their learning style and pace. This is the promise of generative AI in education, making learning more inclusive and effective for all.
Leverage the Experience and Lifelong Learning Knowledge at CyVent

As a security professional, I am driven by intellectual curiosity and a deep, ongoing interest in advanced technology. I am equally passionate about leveraging my knowledge and experience to create safer online environments for business owners.
That's why I founded and why we've built our offerings to focus on a holistic approach to cybersecurity. This is the philosophy that guides our entire team of cybersecurity technologists, former CISOs, senior line executives, and academic thought leaders.
Our team has skillfully assessed cybersecurity solutions with what fits best for each unique client because, as a crew of lifelong learners, we all hold each other to the same standard of being current in the latest science, research, and technological knowledge. Contact CyVent today for a free consultation, and let us put that knowledge and experience into action to better protect your organization.
Looking Ahead: Our Responsibility as School Leaders

As we navigate this journey together, let's ask ourselves: - How can we better integrate AI learning into our board and executive development programs? - What steps can we take to ensure our organizations are prepared for AI-driven disruptions in our industry? - How can we leverage our growing AI knowledge to create sustainable competitive advantages? By embracing lifelong learning in AI, we set a powerful example for our entire organization and pave the way for innovation and growth in the years to come.
Using AI in Business: When to Toggle On and When to Toggle Off

As with all tech innovation, generative AI’s ability to expand business value and increase operational efficiency can be accompanied by an inverse expansion of risk. Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human cognitive functions by machines, and its diverse applications include machine learning and natural language processing. Externally, threat actors leverage AI to attack AI-enhanced cybersecurity tools, leading to an AI vs. AI dynamic that has forced cybersecurity to become pre-emptive, not just preventative. Internally, shadow AI and indiscriminate use of AI tools and platforms can also broaden an organization’s threat surface. Implementing AI strategically within businesses is crucial, requiring a comprehensive approach that includes assessing business needs, selecting appropriate tools, developing team skills, and managing data effectively to optimize operations and enhance customer experiences.
In both cases, being discerning about what generative AI tools to use and when is vital to ensuring a robust cybersecurity stance.
This article will explore the risks of indiscriminately leveraging generative AI in business and offer suggestions on when to use—and not use—generative AI tools.
Introduction to AI in Business

What is Artificial Intelligence and its role in business
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human cognitive functions by machines, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. In the context of business, AI plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer engagement, and driving innovation. AI tools and systems enable businesses to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, ultimately leading to better decision-making and improved outcomes. By integrating AI into various business processes, companies can streamline operations, reduce costs, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving market.
Brief history of AI in business
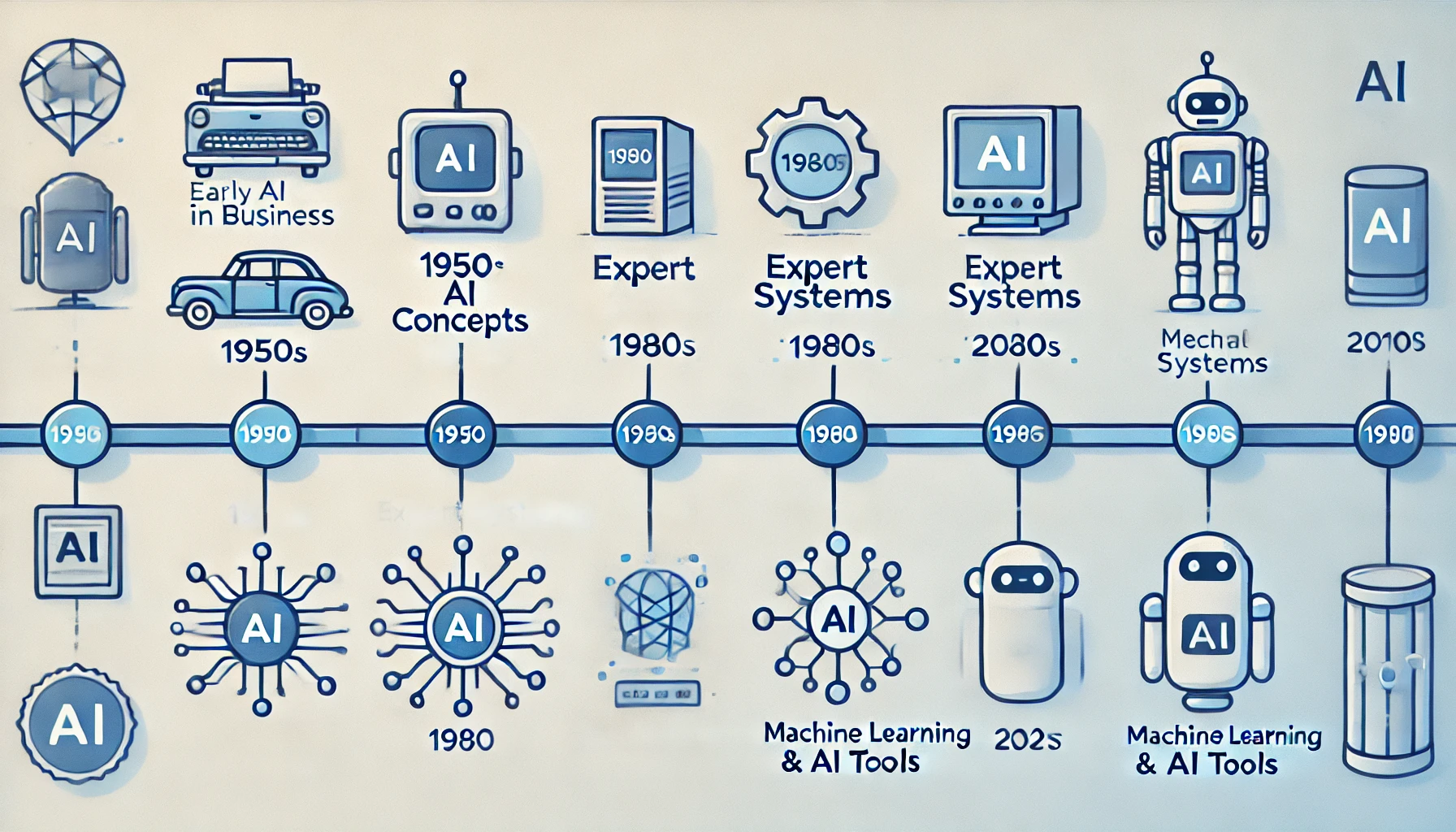
The concept of AI has been around for decades, but its application in business has gained significant momentum in recent years. The first AI-powered tools were introduced in the 1950s, but it wasn’t until the 1980s that AI started to be used in business applications, such as expert systems and decision support systems. The 21st century has seen a significant surge in AI adoption, with the development of machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. Today, AI is an integral part of many business functions, including marketing, sales, customer service, and human resources. This evolution has transformed AI from a theoretical concept into a practical tool that drives business success.
Importance of AI in modern business

In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, AI is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. AI helps businesses stay ahead of the curve by providing them with valuable insights, automating repetitive tasks, and enhancing customer experiences. According to a Harvard Business Review study, companies that adopt AI are more likely to experience significant revenue growth and improved profitability. Moreover, AI enables businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions, identify new opportunities, and mitigate risks. By leveraging AI, businesses can make more informed decisions, optimize their operations, and ultimately achieve better outcomes.
Benefits of AI in Business

Improved Customer Engagement and Experience

AI-powered tools and systems enable businesses to provide personalized and seamless customer experiences. By analyzing customer data and behavior, AI systems can help businesses identify patterns and preferences, leading to targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer engagement. For instance, AI-powered chatbots can help businesses respond to customer inquiries in real-time, while AI-driven recommendation engines can suggest products and services based on customer preferences. According to a study, businesses that use AI-powered customer service tools experience a 25% increase in customer satisfaction.
Additionally, AI can help businesses improve their supply chain operations, inventory management, and risk assessment. By analyzing data from various sources, AI systems can help businesses identify potential bottlenecks, optimize inventory levels, and mitigate risks. For example, AI-powered predictive analytics can help businesses forecast demand, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures that businesses can meet customer demands promptly and effectively.
Overall, AI has the potential to transform businesses in numerous ways, from improving customer engagement and experience to enhancing operational efficiency and driving innovation. As AI continues to evolve, it’s essential for businesses to stay ahead of the curve and leverage AI to gain a competitive edge.

Internal Risks of AI in Business Processes: Shadow AI

Shadow AI, or the use of unapproved AI tools without a company’s knowledge, is rapidly becoming a serious issue in many organizations as employees begin using generative AI-based technology to enhance their performance.
According to a 2024 survey of 150 IT security leaders by HiddenLayer, 61% report shadow AI as a problem within their organizations. Surprisingly, 75% of those security leaders see the threats posed by unauthorized use of third-party AI tools as greater than already-existing cyber threats faced by an organization.
Shadow AI use can lead to proprietary data and IP being fed into external databases. Answers, predictions, and reports may include wildly inaccurate information. Many security vulnerabilities can be inadvertently created by well-meaning but ill-prepared employees, such as when they use a generative AI platform to generate passwords. As generative AI evolves to go beyond aggregating and informing users to take action, internal company risks will only grow.
Human resources AI can help manage employee records, improve recruitment processes, and enhance employee engagement, showcasing its potential to streamline various HR functions.
The solution is not to simply ban AI. The pervasive use of shadow IT in many companies illustrates how bans are, at best, temporarily effective and, at worst, a waste of valuable company resources.
A better solution is to add AI information and education to an organization’s cyber hygiene training program. Reasonable monitoring guardrails may also need to be employed, such as checking employee credit card charges for unauthorized software purchases.
Secondly, accept and embrace the fact AI in business is here to stay. Identify what specific AI-based tools are useful to employees, vet them for risk, and encourage employees to use software, platforms, or tools that pass the test. This creates an internal employee culture in which good cyber hygiene is a matter of course for all employees and is no longer siloed as an “IT issue.”
Finally, balance security with efficiency. If an internal process, such as creating a report or drafting a memo about a developing product, can be done more securely without the assistance of generative AI but also may take longer, the extra time taken in the short run may be worth the time saved dealing with a security breach. Knowing when not to use AI in business is just as important as knowing when to use it.
Using Gen AI for External Risks Assessment

Understanding how to use generative AI tools is no longer optional. Nowhere is this more true than in an organization’s cybersecurity suite.
These tools fill a dangerous gap left by the chronic shortage of cybersecurity professionals. Automated, AI-enhanced tools are the only way to keep up with today’s threat actors, who maliciously use generative AI to create adaptive and evolving threats.

AI helps businesses understand potential threats and vulnerabilities by analyzing data and providing valuable insights. This is where AI in tech has the greatest potential to enhance organizational cybersecurity. Simply assessing the number of endpoints and analyzing potential entry points into a network will no longer suffice to keep a business safe.
Machine learning is evolving into deep learning. This has led to the creation of AI security solutions that react to malware in milliseconds, sometimes before an attack even occurs. Some of these tools will then adapt in real time to prevent potential future attacks. Thus, the peace of mind that stems from automated, continuous monitoring increases with the knowledge that real-time evolution and adaptation to threats is pre-empting them altogether.

Discretion Remains the Better Part of Valor

That said, as with internal processes, there may be times when other components of a comprehensive security approach will not benefit from the use of generative AI. As of yet, there is no advanced technology that can simulate a physical break into a secure section of a building or fully replicate human social engineering (though some platforms with voice-mocking technology are rapidly approaching this point). Though an AI solution may exist, that does not mean it is the right solution for a specific set of high-priority vulnerabilities.
Assessing the correct generative AI tool for your organization’s cybersecurity approach is crucial. Not all generative AI is the same. Technology that uses machine learning rather than deep learning processes is just one example of a key difference. Yes, an organization’s holistic cybersecurity approach will increasingly include generative AI tools. However, what specific tools to use and where to direct them remain important determinants of how robust a security profile is.
While AI can process and analyze data at high speeds, it is intended to support and enhance human decision-making rather than replace the nuanced reasoning and ingenuity inherent to human intelligence.
Remove the Guesswork with CyVent AI Tools

CyVent protects organizations using an overarching philosophy of holistic cybersecurity. Our team of former CISOs, senior line executives, academic thought leaders, and cybersecurity technologists leverages their collective expertise to assess cybersecurity tools, vet potential technology partners, and ultimately create a comprehensive solution specifically designed for the environments they serve.
Whether it's the latest generative AI monitoring platform or a comprehensive, all-in-one cybersecurity suite like Haven, our team has fully investigated and assessed all cybersecurity solutions to ensure they're a good fit for our clients.
Gain peace of mind knowing you have the right tools to protect your organization in place by contacting CyVent today. It takes just one click to schedule a completely confidential call with me and the CyVent team!
~Yuda

Taking a Holistic Approach to Managed Detection and Response
Cybersecurity is no longer just a concern for IT departments and the executive team — it is a critical aspect of business strategy that requires attention and focus from all levels of an organization. Adopting a holistic approach to security and managed detection and response (MDR) is essential to effectively combat evolving threats.
In this blog, we’ll explore the foundational elements of MDR, the importance of a holistic approach, and how advanced technology combined with human intelligence can dramatically enhance your organization’s security.
Managed detection and response services typically provide organizations with threat detection, incident response, and continuous monitoring. Unlike more reactive security measures like firewalls, antivirus, or anti-malware, MDR is proactive, attempting to identify and mitigate threats before they cause damage by monitoring and analyzing security events to identify potential threats.
The foundation of effective MDR lies in its ability to adapt to evolving technology and threats. Cyber threats and threat actors are becoming more sophisticated, and attackers are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Artificial Intelligence (AI) brings about additional tools for threat actors, along with opportunities for security teams to improve their defenses. MDR services must, therefore, be flexible and capable of evolving alongside these trends.
The Need for Managed Detection and Response

In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations face an unprecedented number of threats, from sophisticated malware to targeted attacks. The sheer volume and complexity of these security threats have made it increasingly difficult for security teams to detect and respond to them effectively. This is where Managed Detection and Response (MDR) comes in – a security service that combines advanced technology and human expertise to monitor, detect, and respond to security threats in real-time.
MDR services provide a proactive approach to cybersecurity, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and the expertise of seasoned security professionals, MDR helps organizations identify potential threats before they can cause significant damage. This proactive stance is crucial in today’s environment, where the speed and sophistication of cyberattacks are constantly increasing.
What is Managed Detection and Response?

Managed Detection and Response (MDR) is a comprehensive security service that provides organizations with proactive threat hunting, rapid incident response, and round-the-clock monitoring. Unlike traditional managed security service providers (MSSPs), which typically focus on monitoring and alerting, MDR services actively engage in response actions to neutralize threats.
MDR services utilize advanced technologies and tools to provide a seamless and effective defense against cyber threats. These services include continuous monitoring of network traffic, endpoints, and other critical systems, as well as the use of threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging threats. By combining these advanced technologies with human expertise, MDR services offer a robust and proactive approach to cybersecurity.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach in MDR and Security

Taking a holistic approach means considering every aspect of your cybersecurity strategy, similar to a doctor reviewing all elements of a patient’s health prior to making an official diagnosis. It’s not just about having the right tools; it’s about integrating those tools into a cohesive system that works together with the rest of your strategy.
One key benefit of taking a holistic approach is improved visibility, which is crucial for identifying potential threats and understanding their impact on the organization. Effective security operations involve integrating various tools and processes into a cohesive system, enhancing threat detection and risk management while ensuring continuous protection from evolving cyber threats. This approach also streamlines incident response and enhances the effectiveness of security measures, ensuring that all components work seamlessly together to eliminate gaps and detect threats.
Fusing Advanced Technology with Human and Threat Intelligence

While technology plays a crucial role in MDR, it is only part of the equation. Human intelligence is equally important for effectively detecting and responding to threats. The security operations center (SOC) plays a central role in monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats. The fusion of advanced technology and expert analysis creates a powerful combination that enhances the effectiveness of MDR.
Advanced technologies such as generative AI and machine learning (ML) are able to analyze large amounts of data very quickly and accurately. These rapidly advancing technologies can identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a threat. The valuable insights provided by these tools can help human analysts make better-informed decisions at a more rapid pace.
However, technology alone is not enough. Human analysts bring a level of intuition and expertise that machines cannot replicate. They can interpret the data provided by advanced technologies, identify potential threats, and determine the best course of action. This combination of technology and human intelligence creates a more effective and efficient MDR strategy.
Key Components of a Holistic MDR Strategy

A holistic MDR strategy should include several key components, all working together to provide comprehensive protection against cyber threats.
-
Layered, Pre-emptive tools: Like a castle with defense layers of a moat, drawbridge, watchtowers, and armed guards, utilizing multiple layers of security helps to create a robust defense against potential cyberattacks.
-
Cyber Awareness at all Levels of the Org: Security is important for everyone in an organization, from the C-suite to entry-level team members and outside contractors. Establishing a culture of cybersecurity is critical, and regular training and awareness programs to inform your staff of the latest threats and security trends will arm your team with the knowledge they need to be an important layer of defense for your “castle.”
-
Continuous Monitoring: Analyzing network traffic, endpoints, and other critical systems and assets for signs of potential threats. Having consistent monitoring ensures that any suspicious activity is detected quickly, allowing for a swift response from your security team or your managed security provider.
-
Threat Intelligence: Threat intelligence, which can come from vendor feeds, government agencies, open-source tools, forums, and other sources, provides necessary information about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. By incorporating threat intel into an MDR strategy, organizations can better stay ahead of emerging threats and take more proactive measures to protect their systems.
-
Incident Response: A holistic MDR strategy should include a well-defined incident response (IR) plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a potential security breach.
-
Expert Analysis: Human analysts play an extremely important role in interpreting the large amount of data and alerts provided by advanced technologies. Their expertise and intuition are invaluable for identifying and responding to threats effectively.
Multiple departments should be involved in the planning and documentation process for your overall strategy, such as the executive team, IT department, Human Resources, Legal, PR/Communications, Finance, and any other teams that are critical to your company’s operations. Organizations face challenges when adopting advanced security technologies, such as staffing shortages, alert fatigue, and the need for specialized skills to fully leverage and optimize these solutions.
Choosing the Right MDR Provider

Choosing the right MDR provider is crucial to ensuring that your organization’s security needs are met. When selecting an MDR provider, consider the following factors:
-
Expertise and Experience: Look for a provider with a proven track record in cybersecurity and extensive experience in managing security incidents.
-
Range and Depth of Services: Ensure the provider offers a comprehensive suite of MDR services, including threat hunting, incident response, and continuous monitoring.
-
Customization and Flexibility: The provider should offer tailored solutions that can be customized to meet your organization’s unique security needs.
-
Integration with Existing Infrastructure: The MDR services should seamlessly integrate with your existing security tools and infrastructure to create a cohesive security strategy.
-
Reputation and Customer Satisfaction: Research the provider’s reputation and customer reviews to ensure they have a history of delivering high-quality services and customer satisfaction.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that your organization selects an MDR provider that meets its unique security needs and enhances its overall security posture.
Integrating MDR into Business Operations

Here are some best practices to consider when integrating MDR into your overall business operations:
Assess the Maturity Level of Your Current Security Posture
Before implementing an MDR strategy, assessing your current security posture maturity is essential. Identify gaps or weaknesses in your processes and security measures and determine how MDR can help address them.
Develop a Comprehensive Plan
Your comprehensive plan should outline how MDR will be integrated into your business operations. This plan should include details about the technologies and processes that will be used, as well as the roles and responsibilities of team members.
Integrate with Existing Investments
Ensure that all components of your MDR strategy are integrated seamlessly with your existing security systems. This integration will help create a cohesive security approach and ensure no gaps in coverage exist.
Train (and Retrain) Your Team
Provide continuous training for your team members to ensure they understand how to use the MDR tools and processes effectively. Update the training as needed to cover new features, tools, intelligence, and technology.
Continuously Evaluate and Improve
Cybersecurity isn't a rotisserie on an infomercial, so there's no “set it and forget it” option. We all need to continuously evaluate and improve our MDR strategies to ensure they remain effective. Stay current with the latest technologies, threats, and security vulnerabilities, and adjust your plans as needed.
The Role of Security Teams in MDR

Security teams play a critical role in the success of an MDR strategy. They work closely with the MDR provider to ensure that security threats are detected and responded to effectively. Security teams are responsible for:
-
Providing Contextual Knowledge: Security teams bring valuable contextual knowledge and operational expertise that are essential for interpreting threat data and making informed decisions.
-
Collaborating on Strategy: They collaborate with the MDR provider to develop a comprehensive security strategy that aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
-
Integrating Services: Security teams ensure that MDR services are seamlessly integrated with existing security infrastructure and tools, creating a unified defense system.
-
Responding to Incidents: They play a crucial role in responding to security incidents quickly and effectively, minimizing the impact on the organization.
By working together, security teams and MDR providers can achieve a more resilient and effective cybersecurity posture, ensuring that the organization is well-protected against advanced threats.
MDR and Compliance

MDR services can help organizations meet compliance requirements by providing a comprehensive security solution that includes threat detection, incident response, and continuous monitoring. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR is critical for many organizations, and MDR services can play a key role in achieving and maintaining compliance.
MDR services provide real-time monitoring and threat detection, ensuring that any security incidents are identified and addressed promptly. They also offer detailed reporting and analytics, which are essential for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements. Additionally, MDR services help ensure that security controls are in place and operating effectively, providing organizations with the confidence that they are meeting their compliance obligations.
By leveraging MDR services, organizations can ensure that they are not only meeting compliance requirements but also maintaining a robust security posture that protects their critical assets and data.
A Unified and Holistic Approach to Security

Adopting a holistic approach to managed detection and response is essential for protecting your organization's assets. By integrating advanced technology with human intelligence, you can create a robust security program that effectively detects and responds to threats.
works closely with leading cutting-edge specialists to offer a unified and holistic security strategy, providing comprehensive protection against cyber threats and helping organizations maximize their current security investments.
CyVent's Holistic Security Strategy
CyVent, a boutique advisory firm and solutions provider founded in 2018, focuses on integrating advanced technologies with human intelligence. Our company works with each organization to holistically review their unique needs and helps security teams select the right cybersecurity solutions at the right price for their specific situation.
If you're interested in learning more about our unified approach or the other services that CyVent can provide, book a strategy call with me HERE. Our team is passionate about helping organizations accelerate their transition to an AI-driven preventive posture focused on pre-empting breaches rather than reacting to them. Let's chat!
~Yuda
According to the Computer Security Resource Center definition, Phishing is “a technique for attempting to acquire sensitive data, such as bank account numbers, through a fraudulent solicitation in email or on a website, in which the perpetrator masquerades as a legitimate business or reputable person”. This scam is increasingly common and has devastating consequences for companies.
According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021, Phishing was the second costliest average total cost of the 10 initial attack vectors in the study, at $4.65 million. Furthermore, phishing was the second most frequent initial attack vector, being the gateway to 17% of threats.
The different types of Phishing:
There are different types of phishing. Below, we list some of the most common:
Email Phishing: attacks carried out through messages via email, using fake domains, which imitate those of real companies. It can trick the victim into clicking on a malicious website, making a suspicious download, or tricking them into sending information.
Spear Phishing: While Email Phishing is sent in bulk, for many people, Spear Phishing is personalized, through an email with personal information from the person receiving the message. With this, the chances of the victim falling for the scam is much greater.
Whaling: This Phishing scam targets the “big fish”, meaning the company's top executives. These people usually have a lot of information available on the internet. With dedication and study, scammers manage to mount a very believable bait, which increases the chances of the victim falling for the scam. This type of attack is worrying, as CEOs and C-Levels have access to especially sensitive company information.
Voice Phishing: Voice simulation programs are getting more and more sophisticated. Through this type of resource, scammers are able to simulate voice messages and even phone calls, posing as banking institutions, for example, to collect information or practice scams.
Smishing: This scam involves fake SMS messages. Scammers usually use information from leaks, or information collected from research on social networks, to make the scam seem more real.
These Phishing messages typically follow patterns such as:
- Sense of urgency
- Presence of writing errors
- Unusual requests such as payments or credential information
- Use of non-standard company logos
Given the importance of this threat, here are some strategies that can help your company protect itself from scams:
Tips to protect your business from Phishing Scams:
Qualified and constant training of employees
Keeping employees trained and on the lookout is critical to ensuring a functional end-to-end cybersecurity strategy. Attacks by criminals are increasingly sophisticated, ranging from viruses disguised as attachments to well-rehearsed phone calls.
According to Google's Transparency Report, 46,000 new phishing websites were created every week in 2020.
Employees need to know the dangers, the risks of attacks, and the correct procedures for acting in a phishing situation.
This training can be done by the internal cybersecurity and technology team or delivered automatically by a partner company through short 2-3 minute videos.
Controlled tests
Sending controlled tests allows you to identify the extent to which your company is susceptible to attacks. In addition, fictitious attacks give clues to where the biggest vulnerabilities are and which aspects of cybersecurity the company should strengthen.
A good password strategy
Passwords are a particularly sensitive topic when it comes to phishing. Without the correct management of passwords, with single access, the hacker can have control over several logins. Thus, in addition to training your employees to create strong passwords, it is important to raise awareness about the use of unique passwords for each access, reducing damage in the event of an attack.
Install good email protection solutions
The corporation can invest in efficient solutions to stop suspicious messages and requests through its inbound channels. These malicious emails are blocked and tested by the tools, preventing the scam from reaching the recipient.
CyVent proudly offers Haven, a managed protection, detection, and response solution as a service made for businesses of all sizes, providing enterprise-class security protection, along with controls, management, and monitoring options, with an excellent protection program for your endpoints, your network and your emails.
Use the principle of least privilege
Restricting server access is also a good alternative to protect information. Employees should have access to basic servers, accessing servers with more important information only when necessary. That way, in case of phishing, the threats are found.
The problems your company faces are unique. So your answer should be too. With CyVent you have expert support, cutting-edge software, and access to rigorously selected solutions with 24/7 monitoring.
Book a call: www.cyvent.com/contact-us
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the world, and cybersecurity is no exception.
Autonomous threat monitoring, prevention, detection, and remediation solutions are necessities in a highly dynamic threat environment. AI solutions are also invaluable in the analysis of mass-collected data, such as the thousands of potential security alerts that SIEMs generate.
Unfortunately, the same features of AI that make it ideal for building smart cyber defenses have also started to be used by bad actors to launch smart cyber attacks.
Deep fakes mean deep trouble
AI and Machine Learning (ML) are very well-suited to automating attacks that are launched at scale, such as phishing campaigns, packet sniffing, and vulnerability hunting.
Advanced smart cyber threats aren’t purely hypothetical. Earlier this year, a European energy company lost $243,000 in a scam where hackers used AI-based software to create an audio “deep fake” of the firm’s chief executive. This was the first known incident of a successful financial scam involving an audio deep fake, and there have been many more reported incidents since then, especially as the technical and financial barriers to entry are lowered. Fortunately, AI vendors are developing solutions that are less expensive and more accessible to cyber defense teams.
5 Steps to defeating smart cyberattacks
The fact that hackers are co-opting AI is not an indicator that cybersecurity technologies are flawed or unsafe. Every new and emerging technology that businesses embrace is usually put to the test by hackers, and every new system or device connected to an enterprise data environment expands the potential attack surface. Consider the myriad of threats to IoT devices, mobile apps, and cloud software and services.
Here are five steps that enterprises can take to defend themselves against smart cyberattacks .
1- Don’t expect miracles from AI security solutions
There is no such thing as a security solution, even an AI-powered solution, that will render an entire system impenetrable from all angles. Despite the growing number of advanced tools, there is still no such thing as software that will replace skilled security personnel. AI security solutions are tools that make security personnel more efficient and effective by freeing them from mundane and tedious tasks so that they can focus on higher-level work that requires human intervention, such as investigating and responding to incidents flagged by the system. Learn more about what you can expect from AI security solutions in our recent blog article "Artificial Intelligence and Information Security: Fact vs Fiction".
2- Harden AI systems against adversarial attacks
In addition to using AI to build better cyberattack tools, hackers attack AI-powered security systems themselves. One common method is to launch what researchers call adversarial attacks on machine learning algorithms.
ML algorithms “learn” by examining training data; in the case of a security system, the algorithms are “learning” the difference between safe vs. malicious files, normal and anomalous network behavior. Hackers can turn the training process against itself by feeding false data into a security system to “teach” it that certain malicious activity is baseline behavior and should be ignored. Sometimes, even small changes can significantly impact a system’s behavior and output. Enterprises should anticipate adversarial attacks and take steps to harden their AI systems against injections of false or low-quality data using such methods as adversarial training and defensive distillation.
Recent developments in deep learning are enabling superior accuracy and near-zero false positives compared to machine learning-based defenses. Just as in natural language processing, image recognition, bio-informatics and autonomous driving, deep learning neural networks are way superior in terms of eliminating the need for manual extraction, handcrafted features, misleading readings and noise in the raw data. Forward-looking security teams would be well served by evaluating and adding such tools to their arsenal.
3- Fight deep fakes with multi-layered identity verification
The emergence of highly realistic phony voice prints and other deep fakes illustrates the folly of depending on biometrics as a sole authentication factor, or on any sole verification factor. There is no replacement for multi-factor authentication that includes a strong, randomly generated password as one of the factors.
4- Shore up on cybersecurity basics
“AI gone bad” cyber attacks may grab headlines, but most successful cyber attacks are traced back to decidedly low-tech social engineering techniques, such as phishing emails, or a mistake made by a company insider, such as a misconfigured cloud storage folder. Fundamental proactive security defenses, such as employee cybersecurity awareness training, role-based access control based on the principle of least privilege, firewalls, and making sure that operating systems and software are promptly patched when updates are released not only shore up the enterprise against less exotic attacks but also help prevent smart cyber attacks.
5- Never let down your guard
Cybersecurity is not a matter of “set it and forget it.” New cyber threats and vulnerabilities emerge literally daily; the moment one defense is shored up, hackers find another way in. Preventing cyber attacks requires a solid cyber security policy and constant vigilance, including periodic risk assessments, penetration testing, vulnerability scanning and evaluating new tools.
Why a Prevention-First Mindset Has Made a Comeback in Cybersecurity
Advanced persistent threats (ATP) are a significant cybersecurity concern for the modern-day enterprise. Once inside the perimeter, ATPs either expand quickly, causing the loss of data, interruptions to operations, and more, or stay dormant for long periods of time.
These threats require an answer, one that detection-based tools are failing to provide. New solutions, however, are making it possible to prevent cyber threats in real-time, before they can execute or access and hide in wait on a company’s network.
Sealing the Perimeter by Focusing on Prevention
Emerging technologies have finally outstripped the capabilities of detection-based tools, and prevention is now making a comeback in cybersecurity. The most significant advance is the advent of deep learning, a form of artificial intelligence that is being deployed to successfully detect never-before seen malware, zero-day, ransomware, and APT attacks.
Deep Instinct, a CyVent partner, is leading the charge, making it possible pre-empt attacks before they execute rather than trying to hunt, identify, analyze, recover and remediate. As a result, prevention has immediate payback and ROI, eliminating post-breach wheel spinning and false alerts that are holding security teams back.
Already, Deep Instinct’s solutions has proven capable of stopping known and unknown threats in “zero-time.” In a Threat Prevention Evaluation Report from SE Labs, Deep Instinct achieved an industry-first 100% prevention rate and zero false-positives.
Cyber Security Prevention: Why Detection Alone Is Not Enough
Detection-based tools, on their own, simply can’t provide the level of security needed to keep an organization secure. On average, most threats go undetected for upward of 100 days. Because detection-based tools rely on signatures, threats that have yet to be seen readily slip through traditional defenses. A staggering 360,000 new malicious files are detected every day. Breaches will remain a daily occurrence until cybersecurity tools are able to block new threats as quickly as they evolve.
Security professionals also realize that, besides the fear of a major security incident, predicting threats based on machine learning, heuristics, or file reputation provide less-than-perfect accuracy. Security teams are facing a huge volume of false alerts, more than they can realistically manage. The cost of chasing alerts, the reality of overstretched security teams, and the cybersecurity talent gap are all factors causing security professionals to rethink the balance between detection and prevention.
Preparing for the Next Era of Cyber Threats
Threats that lurk on networks for sometimes months at a time are a grave danger that need addressing. Recent tales of the TRITON malware framework show just how deadly ATPs can be, and even the United States power grid is not immune. The question for security teams is how to prevent threats from ever entering a network in the first place. Many are starting to look to a prevention-first strategy that can enhance security for the current threat landscape. With the era of AI versus AI in cybersecurity fast approaching, it’s security tools like Deep Instinct’s that are the way of the future.
Prevention, however, does not replace detection and response. As with most areas, balance is necessary. Organizations can supplement existing defenses with deep learning technology to prevent attacks with high accuracy before they can cause harm. The reduction in costs and time for an IT team is worth the investment.
Learn more about building a cybersecurity prevention strategy in the white paper Reinventing Cybersecurity Prevention with Deep Learning from Deep Instinct.
Artificial Intelligence and Information Security: Fact vs Fiction
Machine learning, deep learning, generative adversarial networks and other AI technologies have burst onto the cybersecurity scene over the last year. Software vendors and MSSPs are scrambling to bring their particular flavor of AI cyber security to market and claim their stake as industry leaders.
While AI has quickly become table stakes for an effective security posture, some of it can also seem to be overhyped in some respects. In this post, we’ll aim to cut through the superlatives and provide a few thoughts on the role of artificial intelligence in cyber security.
Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security Does Not Replace Traditional Tools
By claiming that AI will replace traditional tools while lowering labor costs and probably making coffee at the same time, some advertising has put AI on a pedestal that it may not have achieved yet.
Here are some things that AI cyber security definitely will not replace. Security teams will still need to keep around:
- Employee training and a security-sensitive culture
- Smart policies and processes
- Qualified architects, managers, engineers, and analysts
- Rock-solid, layered infrastructure with effective controls around it
If you find yourself saying, “Wait, that’s 95% of my security program,” you’re right. Artificial intelligence in cyber security is a complement to a well-run cyber framework, not a replacement for it.
Must-Ask Questions When Evaluating AI Cyber Security Tools
We all have seen that technology can be promoted with grand promises backed by sometimes disappointing results. To avoid a dud in your AI implementation, you may want to sit down with your security team and your vendor rep to go over a few questions:
- How do your AI algorithms actually work? How mature is the technology? What are its blind spots?
- How well does it avoid false positives and false negatives?
- How do you measure the incremental benefits and the expected ROI?
- How will it protect us from insider threats?
- What’s your definition of ‘real-time’?
- Which attack vectors, file type, operating systems do you cover?
- How frequently does it need to be updated?
- How does it handle APT’s, zero-days and zero-hours?
- What outside support are we going to need to implement and maintain this?
- How much additional training will we need to use this effectively?
- Does it produce usable reports that actually mean something?
- What results have your other clients seen from it?
- Does it outperform what I already have, or will it be just another software bloating up my network?
Pitfalls to Avoid When Implementing an AI Cyber Security Solution
Adding software to your organization’s toolkit is rarely a trivial matter, and even less so when you’re dealing with AI. Here are some potential mistakes when deploying an AI cyber security tool:
- Expecting a “set-and-forget” solution that will replace the whole security program: See the first section of this post.
- Thinking that an in-house developed solution will be best-in-show without exploring other available options.
- Expecting that the AI tool won’t require any customization or integration.
- And possibly the most delicate one: Thinking it’ll all work out on automatic pilot without specialized AI expertise on your team or assistance from AI safety experts.
The fact of the matter is that it is no longer viable to delay implementation of robust AI cyber security tools. Bad actors have already started using AI.
A talented cybersecurity team and company-wide awareness trainings go a long way. Artificial intelligence in cyber security simply brings a needed support structure that can assist your teams to prevent attacks and accelerate mitigation if needed. As businesses undergo the digital transformation, it is imperative they also leverage new developments in cyber capabilities and include them in their thinking from the very beginning of their process. Cyber security cannot be an after-thought.
CyVent is a Certified Partner of global leaders in augmented intelligence applied to cybersecurity. Our cutting edge, AI-driven solutions help organizations transition from the classic remediation approach to security to a more pre-emptive posture, which ultimately increases prevention, decreases times-to-resolution and automates cybersecurity operations.
How Deep Learning for Cybersecurity Is Freeing CISOs to Prepare for What's Next
Companies are constantly playing defense against the latest vulnerabilities and cyber threats. New malware variants appear by the second, and tried-and-true attack methods, like phishing and social engineering attacks, remain pervasive.
CISOs, board members, and the general public are well-aware of the dangerous cyber landscape. Yet in the past two years, 60% of businesses have experienced a serious security breach – 31% more than once – according to a recent survey. Advanced persistent threats keep security teams spinning their wheels, trying to hunt, identify, analyze, and remediate in a never-ending cycle. Existing tools based on signatures, heuristics, and reputation tracking are overwhelmed by the sheer volume and the ability of attackers to evolve and bypass defenses.
It’s time for security teams to take another look at prevention vs. remediation, taking advantage of emerging security tools to block attacks before they get downloaded and detonate. Thanks to recent advances in deep learning technology, CISOs can go beyond the prevailing “remediation-first” mindset and achieve the coveted ideal of preventing attacks with near 100% certainty. It may sound like hyperbole, but the technology has been tested and proven and is reimagining cybersecurity for the better.
Where Detection Falls Short, Prevention Enhances Cyber Defenses
By preventing threats, CISOs gain a significant opportunity to reduce wheel spinning and increase the ROI of the business, securing the company’s future while also protecting customers and their data.
Advances in deep learning technology are freeing CISOs from the flood of real breaches and false positives and providing a way to protect the entire attack surface. Deep learning tools are able to block known and unknown threats within milliseconds, before they can download and write to disk. Recently, independent evaluator SE Labs, pitted security provider Deep Instinct’s deep learning solution against a range of high-profile, known malware campaigns and a selection of unknown targeted attacks. The results were eye-opening.
Deep Instinct’s D-Client faced up against malware from well-publicized breaches, fileless targeted attacks, exploits targeted at Microsoft file format vulnerabilities, targeted shellcode injection attacks, and more.
Each threat was successfully prevented pre-execution with no other processes running — resulting in an industry-first 100% prevention rate and zero false-positives. Attackers have learned how to adapt to get past security tools, but now deep learning can act even faster, making zero-time prevention fact rather than a hoped for reality.
Putting CISOs in Full Control of the Security Environment
By adding a deep learning driven pre-emption layer to their environment, CISOs can go beyond sandboxes and signatures to enable threat prevention that hackers cannot evade. Adopting security tools that can detect threats before they execute is also a great enabler of digital transformation. Companies will inevitably need to offer customers more digital products and services and keep sensitive data under lock. The result is increased ROI for the IT department and the company as a whole
When security teams can rely on a tool that can anticipate, identify, and pre-empt threats with confidence, they can shift energy away from remediation and focus on being strategic enablers of business growth. Deep learning driven cyber security can enable zero-time prevention and put CISOs in control — blocking attacks, eliminating false positives and bringing relief from known and unknown threats.
Learn more about Deep Instinct’s solution and how it stood up against known and unknown threats in testing by SE Labs. Get the report here.
 It’s no surprise to anyone that digital threats are evolving and becoming more complex than ever before. As attackers take their game to the next level, an organization’s cybersecurity program should grow and become smarter along with them. The latest step forward in digital defense comes in the form of machine learning and Artificial Intelligence algorithms that combine the reliability of traditional signatures with the power of Big Data analytics.
It’s no surprise to anyone that digital threats are evolving and becoming more complex than ever before. As attackers take their game to the next level, an organization’s cybersecurity program should grow and become smarter along with them. The latest step forward in digital defense comes in the form of machine learning and Artificial Intelligence algorithms that combine the reliability of traditional signatures with the power of Big Data analytics.
Legacy Tools No Longer the Answer to Growing Threats
With the ever-increasing sophistication of today’s security threats, traditional layers of defense like SIEMs, IDS/IPS, and antimalware applications are no longer sufficient. While these tools are certainly effective at thwarting routine port scans or spam emails, the smart security administrator needs to add another layer of security to be truly protected from advanced attacks. Signature-based defenses can’t scale fast enough or stay up to date with critical threats like zero-day attacks or a targeted phishing campaign, and reactive security programs are an open invitation for a data breach. While a business can add more resources to its SOC, or invest in the most engaging security awareness program, an organization’s defense is only as strong as the tools used in that defense. The reality is that security programs built on tools from as recent as 3-4 years ago are already outdated in the face of today’s threats.
Combining Traditional Defenses With Modern Data Analytics
What is the answer to the increasing complexity of these attacks? By pairing the usefulness of legacy solutions with a boost from Big Data, machine learning allows administrators to identify and prevent new or anomalous threats while controlling attacks from traditional threat vectors. Beginning with a baseline of signature files and a sample of normal activity from the network, new security devices can implement machine learning to automatically detect and shut down advanced threats that would otherwise slip past legacy perimeters.
An important component of these AI-driven devices is the ability to aggregate and analyze data from all the environments they are installed in, across multiple customers and industries. For clients who choose to opt-in to the program, smart devices can share their anonymized data in a pool of information from other clients, greatly increasing the samples that algorithms can be based upon. By analyzing data from such a large pool, these devices can leverage predictive analysis to protect an organization from threats that are new to their market but have been seen before in other industries.
In summary, security professionals should be aware that traditional lines of defense are no longer sufficient against today’s evolving threats. Machine intelligence and Big Data are changing the cybersecurity game by combining legacy methods with modern analysis and behavior models and should be seriously considered while building a well-rounded security program.
If you would like to learn more about machine learning in cybersecurity, click here to download "The Enterprise Immune System: Proven Mathematics and Machine Learning for Cyber Defense"...
PHOTO CREDIT: UNSPLASH | JASH CHHABRIA
Responding to Cybersecurity Threats: How to Assess Your Tools and Cyber Strategy
 Cybersecurity is in crisis. Cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and pervasive. Bad actors have access to all the latest technology and tools, including artificial intelligence, for free or very little cost. They have endless time and resources to send out millions of cyberattacks – and need only a single successful attack to reap a windfall. It’s asymmetric warfare, and the attackers’ tools just keep improving.
Cybersecurity is in crisis. Cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and pervasive. Bad actors have access to all the latest technology and tools, including artificial intelligence, for free or very little cost. They have endless time and resources to send out millions of cyberattacks – and need only a single successful attack to reap a windfall. It’s asymmetric warfare, and the attackers’ tools just keep improving.
In response, dozens of new cybersecurity providers seem to enter the market every day. Artificial intelligence, new tools and easy access to information mean that innovation keeps accelerating daily. With cybersecurity threats regularly making headlines, and pressure on companies to secure their data (and customers’ data) growing, new cybersecurity providers barely need to advertise to gain customers’ attention. For the same reasons, venture capitalists are eager to fund cybersecurity firms. The traditional big players in the market are rushing to upgrade their outdated packages. It’s a noisy marketplace, and companies trying to protect their data and systems are confused about how best to do so.
How Companies Are Addressing Cybersecurity Threats
Companies have responded to the crowded cybersecurity marketplace in different ways. Some just bury their heads in the sand, deciding to deal with incursions when they occur, or to hope that they’re too small to be worth targeting with a cyberattack. Others are spending way too much money on cybersecurity, experimenting with every new product that hits the market.
Many companies believe that they already have all the tools they need to combat cybersecurity threats, but haven’t properly patched their existing systems, which need regular updates to combat ever-changing cyber threats. On top of that, many companies experience dozens of little attacks every day, from all sides, and it’s hard to know where to put resources.
But burying your head in the sand or sticking with old tools that don’t counteract today’s cybersecurity threats is simply not an option. And throwing money at whatever strikes a chord isn’t an effective strategy, either.
What Is an Effective Strategy for Managing Cybersecurity Threats?
Resolving the cybersecurity crisis starts with an honest cyber vulnerability assessment, either by your internal experts or by outside experts.
Ultimately, this cyber vulnerability assessment should give you a map of where your company is in terms of cybersecurity. Next, you’ll need a map of where you’re going. Your experts should prepare a plan that:
- Closes your cybersecurity gaps over time
- Analyzes the financial risks of not closing gaps and prioritizes closing the gaps that put the company at the most risk
- Includes a company cybersecurity policy that every employee is expected to follow (much like a dress code or conduct policy)
This cyber vulnerability assessment and plan give you a framework for cybersecurity decisions. Armed with an understanding of your risk profile, your budget, your weaknesses and the consequences of various breaches, your experts should be able to recommend cybersecurity investments that will provide the best ROI for your company. The key is to remain true to this framework, even as new cybersecurity threats rear their ugly heads. Certainly, you want to maintain some flexibility, with strategies adjusting as truly required. But stick with what you know to be important to your business, and let that lead your investment decisions.
Wondering about your ability to respond to cybersecurity threats? Schedule a free, confidential assessment today.
 To thwart cyber attacks, the traditional approach has been to focus on the perimeter to repel intruders. But over time the perimeter has become a sieve. Today’s hackers easily break through it or find ways around it. In fact, a new study by RiskIQ estimates the cost cybercrime at $856,000 per minute. AI cybersecurity solutions directly address these challenges, which is why many now view the technology as the future of cybersecurity.
To thwart cyber attacks, the traditional approach has been to focus on the perimeter to repel intruders. But over time the perimeter has become a sieve. Today’s hackers easily break through it or find ways around it. In fact, a new study by RiskIQ estimates the cost cybercrime at $856,000 per minute. AI cybersecurity solutions directly address these challenges, which is why many now view the technology as the future of cybersecurity.
Going Beyond the Perimeter Is the Future of Cybersecurity
Focusing on defending the perimeter has been akin to wearing a Hazmat suit in a hostile environment: Any small perforation, and you were doomed to unexpected consequences at the hands of hackers who had the time and intellect to play games with your critical assets.
Not only are perimeters fragile and the gap in available talent huge, but most IT teams are often so stretched for resources that they can’t keep up with the updates necessary to protect against the myriad attacks that can penetrate a company’s external defenses. WannaCry was just an example of that.
Over the years, computing speed has grown exponentially –multiplying more than 3,000x since 1991 – to the point where even a $5 Raspberry Pi can now run deep learning algorithms. So it’s not a surprise that, in recent years, focus has shifted to using AI cybersecurity to complement traditional defenses in many ways and neutralize stealthy, unknown threats that may have already breached the perimeter before any irreparable damage to network or data is done.
Applying Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
In AI cybersecurity programs, which are now being embedded in companies’ networks, endpoints and data are evolving into immune systems that allow internal defenses to shorten the dwell-time and pre-empt the devastation that can follow a breach.
While there is no need to abandon the perimeter, today’s smart CISOs are squarely focused on increasing their AI-driven pre-emption capabilities and boosting their own auto-immune systems. Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is by no means perfect yet, but cybercriminals are already using automation and machine learning 24x7x365. In the never-ending cat-and-mouse game, AI is slated to continue gaining ground to build predictive capabilities and strengthen defenses for the foreseeable future.
To learn more about how AI is impacting the future of cybersecurity, download this white paper from Darktrace: Machine Learning in Cybersecurity.
ICS Cybersecurity: Using AI in Operational Technology Security
Updated on May 7, 2019
Recent headlines have been abuzz with ICS experts warning of grid vulnerability to hacking. Digital threat actors have become exceptionally skilled at infiltrating every type of computer network. Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are no different: While ICS networks were generally thought to be more secure due to not communicating outside of the corporate network or on the internet, attackers have managed to compromise them and steal valuable production data.
Some of the most effective tools for ICS cybersecurity are the emerging technologies in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. By combining real-time data monitoring with orchestration and automated response, AI/ML solutions are proving their value when compared to legacy systems and human-intervention driven response times.
A Real-World Example of Using AI for ICS Network Security
At the 2017 Black Hat Europe conference, security research firm CyberX demonstrated how data exfiltration was possible from a supposedly air-gapped ICS network. By delivering a payload of specific ladder logic code into Programmable Logic Controllers, the attack was programmed to send out copies of data through encoded radio signals which can be received by AM radios and analyzed by special-purpose software. As the communication channel is outside the TCP/IP stack, there is no encryption to safeguard the data once it’s captured.
How does AI respond to this threat? In this case, Machine Learning can be used to craft an algorithm which establishes a “normal” state and monitors traffic and configurations to compare against that state. This baseline can include network traffic, equipment settings, and even the source code of PLCs. With its continuous heartbeat checks, the algorithm can detect when the system deviates from the baseline and immediately alert security staff of the change.
Another real-world example involving operational technology security comes very recently from the ransomware attack on Norsk Hyrdo, one of the world’s largest aluminum producers based in Norway. The ransomware infected multiple systems across the organization in a number of locations.The company’s production environments were forced to stop production or change to manual systems. The ransomware supported the changing of administrator passwords, and as the majority of servers were under the same domain, the attack could spread more rapidly than if there had been a combination of network segmentation and separately administered domains. In the case of Norsk, an AI cybersecurity layer would have been able to spot irregularities in system access and lockdown channels before the hackers could manipulate the permissions.
AI and ICS Cybersecurity: Adding Value to Existing Systems
Where does AI fit into your existing ICS network security program? You already have the ICS equipment sectioned off on its own VLAN(s), firewalled, monitored, and protected by IDS/IPS, SIEMs, and other security tools. Where does it make sense to insert AI/ML into the equation?
The biggest advantage of implanting an AI solution for ICS cybersecurity is its real-time response and orchestration. AI tools don’t need to wait for security staff to make a decision. They don’t see a black and white picture of firewall rules which often miss malware traffic flying under the radar, masquerading as “normal” network signals. Machine algorithms can detect abnormal data exchanges and immediately respond to the threat, long before a SOC resource would be alerted. Some AI offerings can even monitor devices that don’t communicate over TCP/IP, creating powerful visibility into non-networked equipment.
A particularly interesting tool to protect industrial control systems is Cyberbit’s ScadaShield, a layered solution to provide full stack ICS network detection, visibility, smart analytics, forensics and response. ScadaShield performs continuous monitoring and detection across the entire attack surface for both IT and OT components and can be combined with SOC automation to trigger workflows that accelerate root cause identification and mitigation.
Large-scale processes operating at critical power generation, electrical transmission, water treatment, and refining sites, as well as major manufacturing plants are more at risk than ever. The good news is that new developments in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have created new ways to protect these systems and improve ICS cybersecurity.
If you haven’t already done so, this is a good time to consider adding an AI/ML solution to your security perimeter to take your prevention and response times to the next level. Click here to contact us if you would like to learn more about artificial intelligence in cyber security.
PHOTO CREDIT: UNSPLASH | RAMÓN SALINERO
Artificial Intelligence and ICS Cybersecurity: Filling Gaps in Operational Technology Security
 Recent headlines have been abuzz with ICS experts warning of grid vulnerability to hacking. Digital threat actors have become exceptionally skilled at infiltrating every type of computer network. Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are no different: While ICS networks were generally thought to be more secure due to not communicating outside of the corporate network or on the internet, attackers have managed to compromise them and steal valuable production data.
Recent headlines have been abuzz with ICS experts warning of grid vulnerability to hacking. Digital threat actors have become exceptionally skilled at infiltrating every type of computer network. Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are no different: While ICS networks were generally thought to be more secure due to not communicating outside of the corporate network or on the internet, attackers have managed to compromise them and steal valuable production data.
Some of the most effective tools for ICS cybersecurity are the emerging technologies in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. By combining real-time data monitoring with orchestration and automated response, AI/ML solutions are proving their value when compared to legacy systems and human-intervention driven response times.
A Real-World Example of Using AI for ICS Network Security
At the last Black Hat Europe conference, security research firm CyberX demonstrated how data exfiltration was possible from a supposedly air-gapped ICS network. By delivering a payload of specific ladder logic code into Programmable Logic Controllers, the attack was programmed to send out copies of data through encoded radio signals which can be received by AM radios and analyzed by special-purpose software. As the communication channel is outside the TCP/IP stack, there is no encryption to safeguard the data once it’s captured.
How does AI respond to this threat? In this case, Machine Learning can be used to craft an algorithm which establishes a “normal” state and monitors traffic and configurations to compare against that state. This baseline can include network traffic, equipment settings, and even the source code of PLCs. With its continuous heartbeat checks, the algorithm can detect when the system deviates from the baseline and immediately alert security staff of the change.
Another real-world example involving operational technology security comes very recently from the ransomware attack on Atlanta’s municipal infrastructure, which involved encrypting city files, locking access to online services, and blocking the city from processing court cases and warrants. This is just the latest in a string of attacks on American cities. Previously, hackers gained access to Dallas’s tornado warning system and set off sirens in the middle of the night. In the case of Atlanta, an AI cybersecurity layer would have been able to spot irregularities in system access and lockdown channels before the hackers could manipulate the permissions.
AI and ICS Cybersecurity: Adding Value to Existing Systems
Where does AI fit into your existing ICS network security program? You already have the ICS equipment sectioned off on its own VLAN(s), firewalled, monitored, and protected by IDS/IPS, SIEMs, and other security tools. Where does it make sense to insert AI/ML into the equation?
The biggest advantage of implanting an AI solution for ICS cybersecurity is its real-time response and orchestration. AI tools don’t need to wait for security staff to make a decision. They don’t see a black and white picture of firewall rules which often miss malware traffic flying under the radar, masquerading as “normal” network signals. Machine algorithms can detect abnormal data exchanges and immediately respond to the threat, long before a SOC resource would be alerted. Some AI offerings can even monitor devices that don’t communicate over TCP/IP, creating powerful visibility into non-networked equipment.
A particularly interesting tool to protect industrial control systems is Cyberbit’s ScadaShield, a layered solution to provide full stack ICS networkdetection, visibility, smart analytics, forensics and response. ScadaShield performs continuous monitoring and detection across the entire attack surface for both IT and OT components and can be combined with SOC automation to trigger workflows that accelerate root cause identification and mitigation.
Large-scale processes operating at critical power generation, electrical transmission, water treatment, and refining sites, as well as major manufacturing plants are more at risk than ever. The good news is that new developments in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have created new ways to protect these systems and improve ICS cybersecurity.
If you haven’t already done so, this is a good time to consider adding an AI/ML solution to your security perimeter to take your prevention and response times to the next level. Click here to get in touch with our team today.
PHOTO CREDIT: UNSPLASH | RAMÓN SALINERO
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security: Separating Fact from Fiction
 Machine learning and artificial intelligence have exploded onto the cybersecurity scene over the last year. Software vendors and MSSPs are scrambling to bring their particular flavor of AI cyber security to market and claim their stake as industry leaders.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence have exploded onto the cybersecurity scene over the last year. Software vendors and MSSPs are scrambling to bring their particular flavor of AI cyber security to market and claim their stake as industry leaders.
While AI has quickly become table stakes for an effective security posture, some of it can also seem to be overhyped in some respects. In this post, we’ll aim to cut through the superlatives and provide a few thoughts on the role of artificial intelligence in cyber security.
Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security Does Not Replace Traditional Tools
By claiming that AI will replace traditional tools while lowering labor costs and probably making coffee at the same time, some advertising has put AI on a pedestal that it may not have achieved yet.
Here are some things that AI cyber security definitely will not replace. Security teams will still need to keep around:
- Employee training and a security-sensitive culture
- Smart policies and processes
- Qualified architects, managers, engineers, and analysts
- Rock-solid, layered infrastructure with effective controls around it
If you find yourself saying, “Wait, that’s 95% of my security program,” you’re right. Artificial intelligence in cyber security is a complement to a well-run cyber framework, not a replacement for it.
Must-Ask Questions When Evaluating AI Cyber Security Tools
We all have seen that technology can be promoted with grand promises backed by sometimes disappointing results. To avoid a dud in your AI implementation, you may want to sit down with your security team and your vendor rep to go over a few questions:
- How do your AI algorithms actually work? How mature is the technology? What are its blind spots?
- How well does it avoid false positives and false negatives?
- How do you measure the incremental benefits and the expected ROI?
- What outside support are we going to need to implement and maintain this?
- How much additional training will we need to use this effectively?
- Does it produce usable reports that actually mean something?
- What results have your other clients seen from it?
- Does it outperform what I already have, or will it be just another software bloating up my network?
Pitfalls to Avoid When Implementing an AI Cyber Security Solution
Adding software to your organization’s toolkit is rarely a trivial matter, and even less so when you’re dealing with AI. Here are some potential mistakes when deploying an AI cyber security tool:
- Expecting a “set-and-forget” solution that will replace the whole security program: See the first section of this post.
- Thinking that an in-house developed solution will be best-in-show without exploring other available options.
- Expecting that the AI tool won’t require any customization or integration.
- And possibly the most delicate one: Thinking it’ll all work out on automatic pilot without specialized AI expertise on your team or assistance from AI safety experts.
The fact of the matter is that it is no longer viable to delay implementation of robust AI cyber security tools. Bad actors have already started using AI.
A talented cybersecurity team and company-wide awareness trainings go a long way. Artificial intelligence in cyber security simply brings a needed support structure that can assist your teams to prevent attacks and accelerate mitigation if needed. As businesses undergo the digital transformation, it is imperative they also leverage new developments in cyber capabilities.
CyVent is a Certified Partner of Darktrace, a global leader in machine learning applied to cybersecurity, whose technology can detect and autonomously respond to cyber threats that legacy systems miss. Learn more about Darktrace’s capabilities in this white paper.
Updated on May 7, 2019
It’s no surprise to anyone that digital threats are evolving and becoming more complex than ever before. As attackers take their game to the next level, an organization’s cybersecurity program should grow and become smarter along with them. The latest step forward in digital defense comes in the form of machine learning and Artificial Intelligence algorithms that combine the reliability of traditional signatures with the power of Big Data analytics.
Legacy Tools No Longer the Answer to Growing Threats
With the ever-increasing sophistication of today’s security threats, traditional layers of defense like SIEMs, IDS/IPS, and antimalware applications are no longer sufficient. While these tools are certainly effective at thwarting routine port scans or spam emails, the smart security administrator needs to add another layer of security to be truly protected from advanced attacks. Signature-based defenses can’t scale fast enough or stay up to date with critical threats like zero-day attacks or a targeted phishing campaign, and reactive security programs are an open invitation for a data breach. While a business can add more resources to its SOC, or invest in the most engaging security awareness program, an organization’s defense is only as strong as the tools used in that defense. The reality is that security programs built on tools from as recent as 3-4 years ago are already outdated in the face of today’s threats.
Combining Traditional Defenses With Modern Data Analytics
What is the answer to the increasing complexity of these attacks? By pairing the usefulness of legacy solutions with a boost from Big Data, machine learning allows administrators to identify and prevent new or anomalous threats while controlling attacks from traditional threat vectors. Beginning with a baseline of signature files and a sample of normal activity from the network, new security devices can implement machine learning to automatically detect and shut down advanced threats that would otherwise slip past legacy perimeters.
An important component of these AI-driven devices is the ability to aggregate and analyze data from all the environments they are installed in, across multiple customers and industries. For clients who choose to opt-in to the program, smart devices can share their anonymized data in a pool of information from other clients, greatly increasing the samples that algorithms can be based upon. By analyzing data from such a large pool, these devices can leverage predictive analysis to protect an organization from threats that are new to their market but have been seen before in other industries.
In summary, security professionals should be aware that traditional lines of defense are no longer sufficient against today’s evolving threats. Machine intelligence and Big Data are changing the cybersecurity game by combining legacy methods with modern analysis and behavior models and should be seriously considered while building a well-rounded security program. Click here to learn more about machine learning in cyber security.
PHOTO CREDIT: UNSPLASH | JASH CHHABRIA
Updated on May 7, 2019
Every other day, we hear disclosures about some new security breach that leads to damaged reputations, executive resignations and plummeting stock values. While It is tempting to become a wee-bit sarcastic and ‘normalize’ this state of affairs, the danger of cyber attacks can’t be understated. The gap between time to exfiltration vs time to quarantine is growing in favor of attackers. Thought leaders and Trillion-Dollar loss projections reinforce that information warfare is a serious threat that’s quickly becoming the #1 danger for businesses, governments and even individual liberties.
What is the Role of Cybersecurity?
Throw in a dizzying array of new technologies and new vendors, and it‘s no wonder cyber security executives, CFOs and CEO’s feel growing levels of pressure. What we all need at this time is a change in attitude: The role of cyber security is to enable the business to reach its goals, not to be the goal in and of itself. No business exists for the sake of having an unbreachable security program, if such a thing can even be built. On the contrary, a good security program drives and supports the organization to reach its strategic goals.
In this non-stop ‘spy vs. spy’ game between good guys and bad actors, the solution is not to keep adding one shiny tool after another but rather focusing on a well-thought out strategy that includes multiple prongs: (a) Periodic audits, strong fundamentals, clear policies and well-trained team members (b) adding advanced tools to automate, orchestrate and streamline processes while reducing costs, and (c) including cyber security within the C-level risk management view that balances acceptable exposure levels, qualifies the required investments and takes advantage of available risk transfer options.
What is the role of a trusted Cyber Security Solutions Provider?
Within this quickly changing environment, a trusted partner’s role is to help the clients reduce anxiety, become better risks and increase peace of mind.
A trustworthy partner will sit down and fully understand your needs before talking about any kind of product lineup. If you have security questions, contact us and let’s make a plan that works for you.
PHOTO CREDIT: UNSPLASH | TASKIN ASHIQ
The Importance of a Cyber Security Program Built on Strategy, Not Fear
 Every other day, we hear disclosures about some new security breach that leads to damaged reputations, executive resignations and plummeting stock values. While It is tempting to become a wee-bit sarcastic and ‘normalize’ this state of affairs, the danger of cyber attacks can’t be understated. The gap between time to exfiltration vs time to quarantine is growing in favor of attackers. Thought leaders and Trillion-Dollar loss projections reinforce that information warfare is a serious threat that’s quickly becoming the #1 danger for businesses, governments and even individual liberties.
Every other day, we hear disclosures about some new security breach that leads to damaged reputations, executive resignations and plummeting stock values. While It is tempting to become a wee-bit sarcastic and ‘normalize’ this state of affairs, the danger of cyber attacks can’t be understated. The gap between time to exfiltration vs time to quarantine is growing in favor of attackers. Thought leaders and Trillion-Dollar loss projections reinforce that information warfare is a serious threat that’s quickly becoming the #1 danger for businesses, governments and even individual liberties.
What is the Role of Cybersecurity?
Throw in a dizzying array of new technologies and new vendors, and it‘s no wonder cyber security executives, CFOs and CEO’s feel growing levels of pressure. What we all need at this time is a change in attitude: The role of cyber security is to enable the business to reach its goals, not to be the goal in and of itself. No business exists for the sake of having an unbreachable security program, if such a thing can even be built. On the contrary, a good security program drives and supports the organization to reach its strategic goals.
In this non-stop ‘spy vs. spy’ game between good guys and bad actors, the solution is not to keep adding one shiny tool after another but rather focusing on a well-thought out strategy that includes multiple prongs: (a) Periodic audits, strong fundamentals, clear policies and well-trained team members (b) adding advanced tools to automate, orchestrate and streamline processes while reducing costs, and (c) including cyber security within the C-level risk management view that balances acceptable exposure levels, qualifies the required investments and takes advantage of available risk transfer options.
What is the role of a trusted Cyber Security Solutions Provider?
Within this quickly changing environment, a trusted partner’s role is to help the clients reduce anxiety, become better risks and increase peace of mind.
A trustworthy partner will sit down and fully understand your needs before talking about any kind of product lineup. If you have security questions, contact us and let’s make a plan that works for you.




